- Accueil
- 130 adaptation vers l'inclusion
- Validity and reliability of the patient assessment on chronic illness care (PACIC) questionnaire: the Malay version, BMC Primary Care
Validity and reliability of the patient assessment on chronic illness care (PACIC) questionnaire: the Malay version, BMC Primary Care
5 (356) · € 32.50 · En Stock
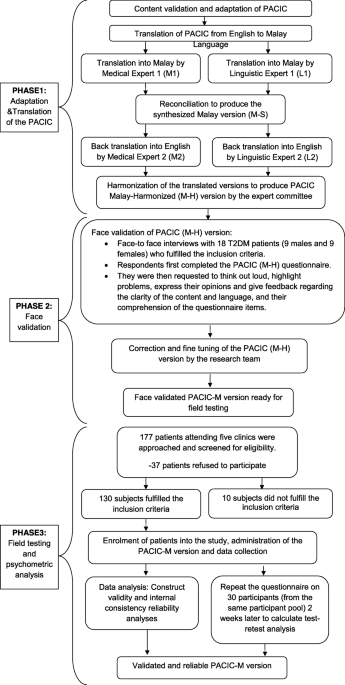
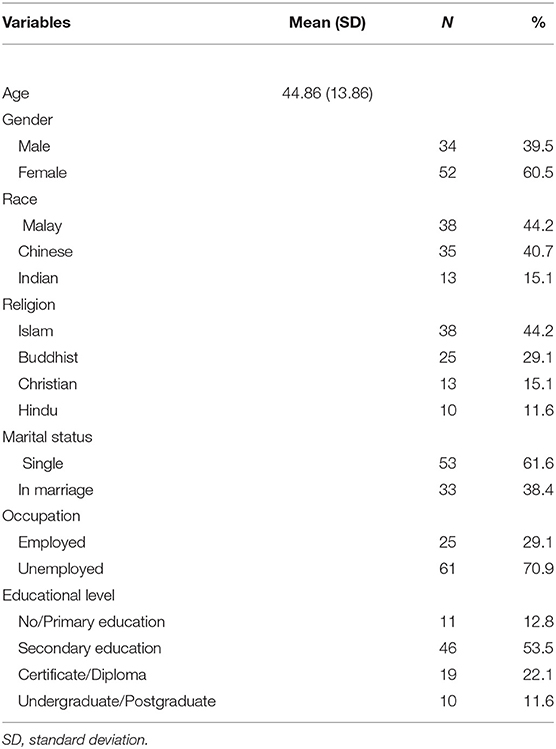
Background Majority of patients with chronic illnesses such as diabetes, receive care at primary care setting. Efforts have been made to restructure diabetes care in the Malaysian primary care setting in accordance with the Chronic Care Model (CCM). The Patient Assessment on Chronic Illness Care (PACIC) is a validated self-report tool to measure the extent to which patients with chronic illness receive care that aligns with the CCM. To date, no validated tool is available to evaluate healthcare delivery based on the CCM in the Malay language. Thus, the study aimed to translate the PACIC into the Malay language and validate the questionnaire among patients with diabetes in the Malaysian public primary care setting. Methods The English version of the PACIC questionnaire is a 20-item scale measuring five key components, which are patient activation, decision support, goal setting, problem solving and follow-up care. The PACIC underwent forward - backward translation and cross cultural adaptation process to produce the PACIC-Malay version (PACIC-M). Reliability was tested using internal consistencies and test-retest reliability analyses, while construct validity was tested using the exploratory factor analysis (EFA). Results The content of PACIC-M and the original version were conceptually equivalent. Overall, the internal consistency by Cronbach’s α was .94 and the intra-class correlation coefficient was .93. One item was deleted (item 1) when the factor loading was < 0.4. The factor analyses using promax identified three components (‘Goal Setting/Tailoring and Problem solving/Contextual’, ‘follow-up/coordination’ and ‘patient activation and delivery system design/ decision support’); explaining 61.2% of the variation. The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) was 0.93 and Bartlett’s test of sphericity was p = .000. Therefore, the final version of the PACIC-M consisted of 19 items, framed within three components. Conclusion The findings demonstrated that the PACIC-M measured different dimensions from the English version of PACIC. It is however; highly reliable and valid to be used in assessing three CCM model subscales. Further confirmatory factor analysis of PACIC-M should be conducted to confirm this new model.

PDF) Traditional and complementary medicine (TCM) usage and its association with Patient Assessment of Chronic Illness Care (PACIC) among individuals with metabolic syndrome in primary care
Frontiers Shared Decision-Making and Role Preference Among Patients With Schizophrenia in Malaysia: A Cross-Sectional Study
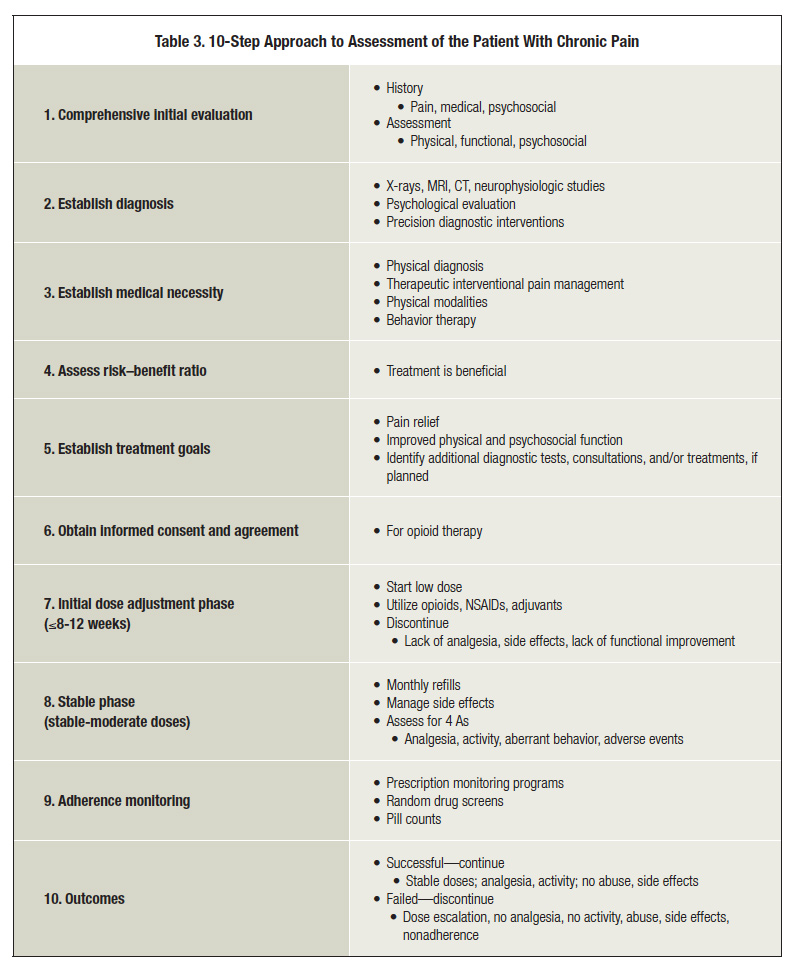
Guide to Chronic Pain Assessment Tools

Organisational models in primary health care to manage chronic conditions: A scoping review - Longhini - 2022 - Health & Social Care in the Community - Wiley Online Library

Traditional and complementary medicine (TCM) usage and its association with Patient Assessment of Chronic Illness Care (PACIC) among individuals with metabolic syndrome in primary care, BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies

PDF] Adaptation, data quality and confirmatory factor analysis of the Danish version of the PACIC questionnaire.

PDF) Structure and measurement properties of the Patient Assessment of Chronic Illness Care instrument

Interventions for improving outcomes in patients with multimorbidity in primary care and community settings - Smith, SM - 2021

Perceived quality of care among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the north east region of peninsular Malaysia, BMC Public Health

PDF) Validity and reliability of the Patient Assessment on Chronic Illness Care (PACIC) questionnaire among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Malaysia: English version

Measuring Self-Care in Persons With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review - Yan Lu, Jiayun Xu, Weigang Zhao, Hae-Ra Han, 2016

(PDF) Validity and reliability of the patient assessment on chronic illness care (PACIC) questionnaire: The Malay version